In Afar region, numerous investment and tourism attractions create significant opportunities to attract both domestic and international investors. The following list highlights some of these potentials:



Afar region boasts an estimated livestock population, including:
It is estimated that the pastoral sector contributes significantly, raising 40% of the cattle, 75% of the goats, 30% of the sheep, and 100% of the camels. Pastoral areas make up over 90% of the annual legal exports of live and processed animals.
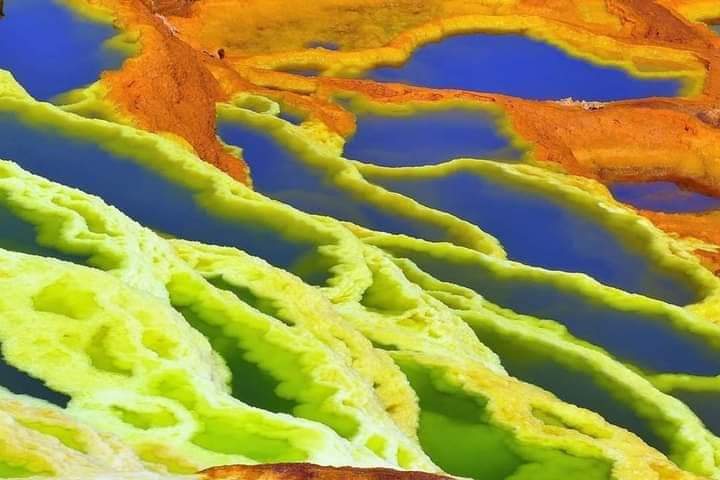
The Afar region has a huge potential for mineral resources, as the region has abundant and diverse mineral deposits, such as:
| Mineral | Reserve | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Potash | Above 1.3 billion tons | Dallol area |
| Bromine, chlorine, lithium | Unknown | Afdera and Asale lakes |
| Gold | 50-250 tons | Various locations |
| Silver | 10-50 tons | Various locations |
| Manganese | 1-10 million tons | Various locations |
| Marble | Above 50 million tons | Various locations |
| Nickel | 0.2-2 million tons | Various locations |
| Cobalt | Unknown | Various locations |
| Quartz | 0.1-1 million tons | Various locations |
| Salt | 5-50 million tons | Various locations |
The geology of the area is characterized by Neoproterozoic metavolcanic and metasediments, Quaternary alluvial fan deposits and red beds, a transitional zone of mud and salt mixture, and evaporites, which consist of rock salt (commonly halite and potash) and sulfur/sulfides. Currently, two foreign companies are licensed for investment in the exploration of the potash mine.
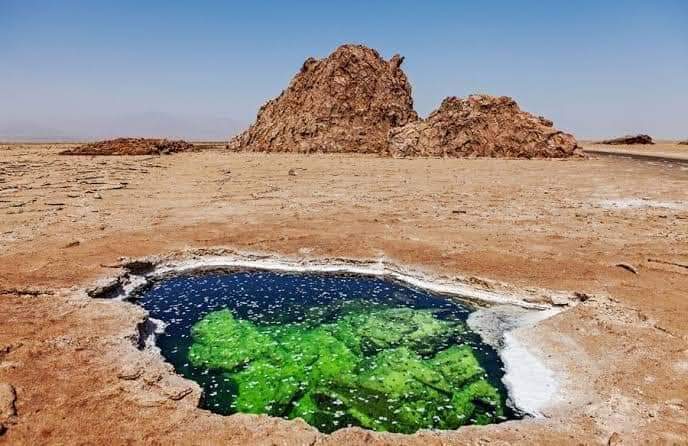
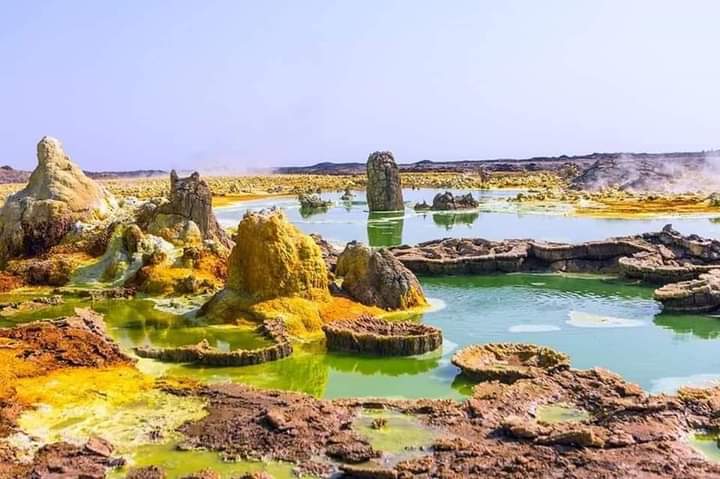
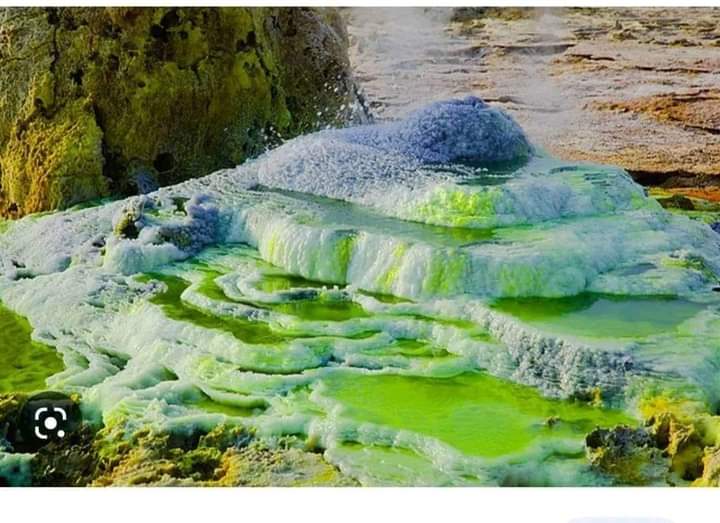
The Afar region has a unique and attractive tourism potential, as the region has various natural and cultural attractions, such as:
The region also has a rich and diverse culture and history, as the region is home to the Afar people, who are known for their nomadic and pastoral lifestyle, and their traditional customs and ceremonies.



At present, the agricultural development of the region is very low. The rain fed agriculture is negligible due to low, unreliable and erratic distribution of rainfall and the irrigation is not that much developed either. However, it has to be known that there is almost 538,361.5 hectares of agricultural potential in the region provided that the regional government is prepared to manage a comprehensive and coordinated approach consisting of good and intensive integrated agricultural development programmes through proper utilization of the natural resources, expansion and development of modern irrigation, well developed infrastructure, etc. are in place. By considering these factors, the current low level of the agricultural production of the region can be undoubtedly being increased within reasonable period of time. If such concerted effort is fully practiced, commercial and industrial crops such as maize (sweet corn), wheat, sorghum, groundnut (peanut), sesame, mung nuts, cow peas, castor, cotton, sugar cane, sisal, onion, tomato, green beans, water melons, spinach, sweet potatoes, banana and grapes as well as from cumin and coriander are among the potential ones. By considering the potential of the Region, project ideas in the area of cotton production and processing, edible oil from different oil seeds, flour mills of different cereals, tomato plantation and processing and the like are identified. Such activities in effect will create backward and forward linkage effects in the Regional economy.



Ethiopia, particularly Afar, holds enormous potential for mineral raw materials, including salt, potash, and gold. Mining is crucial to Ethiopia's economy, diversifying from agriculture. Gold, gemstones, and industrial minerals are vital commodities for the country's export-oriented growth strategy.
Potash reserves are estimated to be above 1.3 billion tons. Currently, two foreign companies are licensed for investment in the exploration of the potash mine. Most potash is found in the Dallol area located in Afar.


The energy resource base of the region can be classified as modern and traditional energy. Modern energy includes hydropower, geothermal, diesel electricity, hydrocarbon resources, solar energy and wind energy. The traditional energy includes biomass (woody biomass, agri-residues and biogas) and animate energy. Although the Region does not have significant potential for hydropower generation, the region gets 95% of the electricity from the national grid or Inter Connected System (ICS).In addition to the power supplied from hydropower, the Afar region uses diesel electricity. The Afar region is endowed with huge amount of solar energy. Therefore, it is important to consider its utilization in the development programme of the Region. The other energy potential is wind. The Region has a huge amount of geothermal resources which have been well explored and waiting exploitation. The other energy potential in the region is agri-residues, i.e., crops residues and cattle dung etc. It can be a basis for establishing fuel briquette and biogas plants in the rural and urban area of the Region. In general, except in the area of hydropower, the Region has potential of energy resources such as geo thermal, solar, wind and biomass. These resources can be used in the Region if sound energy policies and strategies are formulated. Considering the resources available in the region, projects that could be implemented by the private and public sector are identified. These include solar panel (PV system), solar water heater, and pump and cooker, geothermal plant etc


Join hands with Afar Investment Commission and unlock a world of opportunities. Contact us today to discover how we can assist you in realizing your investment goals in the Afar region.